Electric Field (Discrete and Continuous Charge Distributions)
Electric Field (Discrete and Continuous Charge Distributions): Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Electric Field, Electric Field Due to a Point Charge, Electric Field due to a Large Charged Sheet Using Coulomb's Law & Electric Field near a Conductor etc.
Important Questions on Electric Field (Discrete and Continuous Charge Distributions)
A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges Q. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if
Assertion: Due to two point charges electric field and electric potential cannot be zero at some point simultaneously.
Reason: Field is a vector quantity and potential is a scalar quantity.
Two point charges and are placed some distance apart. If the electric field at the location of be , then that at the location of will be
The maximum field intensity on the axis of a uniformly charged ring of charge and radius will be
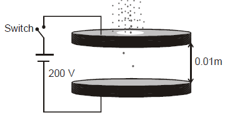
Two large circular discs separated by a distance of are connected to a battery via a switch as shown in the figure. Charged oil drops of density are released through a tiny hole at the center of the top disc. Once some oil drops achieve terminal velocity, the switch is closed to apply a voltage of across the discs. As a result, an oil drop of radius stops moving vertically and floats between the discs. The number of electrons present in this oil drop is ______.(neglect the buoyancy force, take acceleration due to gravity and charge on an electron )
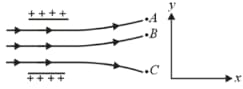
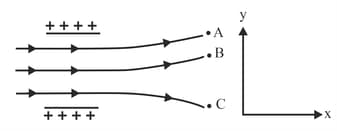
The tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field are shown in the figure. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio?
If the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is zero then
The constant in Coulomb’s law depends on
A metal plates of capacitor of area carries a charge of . Calculate the outward pull on plate (in newton).
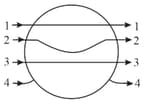
A metallic shpere is placed in a uniform electric field. The line of force follow the path(s) shown in the figure as,
The maximum field intensity on the axis of a uniformly charged ring of charge and radius will be
A thin conducting ring of radius is given a charge . The electric field at the centre of the ring due to the charge on the part of the ring is . The electric field at the centre due to the charge on the part of the ring is
The tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field are shown in the figure. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio?
If the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is zero
The constant in Coulomb’s law depends on
Two point charges of and are apart where will the electric field strength be zero on the line joining the charges from charge
A small metal ball is suspended in an uniform electric field with the help of an insulated thread. If a high energy -ray beam falls on the ball, then the ball
The electric intensity outside a charged sphere of radius at a distance is
The minimum strength of a uniform electric field that can tear a conducting neutral thin-walled sphere into two equal parts is known to be . Then determine the minimum electric field strength required to tear a sphere of one-fourth of the radius with the same wall thickness.
Two mutually perpendicular infinitely long straight conductors carrying uniformly distributed charges of linear densities and are positioned at a distance from each other.
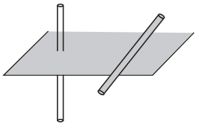
Force between the conductors depends on as